Κατάλογος ηγεμόνων στη Θράκη και τη Δακία
Αυτό το άρθρο απαριθμεί τους ηγεμόνες της Θράκης και της Δακίας και περιλαμβάνει Θράκες, Παίονες, Κέλτες, Δάκες, Σκύθες, Πέρσες ή Αρχαίους Έλληνες μέχρι το σημείο της πτώσης της στη Ρωμαϊκή Αυτοκρατορία, με μερικές μορφές από την ελληνική μυθολογία.
Μυθολογικοί
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Αίμος, έγινε το όρος Αίμος
- Θραξ, γιος του Άρη
- Τεγύριος, θνητός
- Εύμολπος κληρονόμησε ένα βασίλειο από τον Τεγύριο
- Τηρέας, ο βασιλιάς που μετατράπηκε σε τσαλαπετεινό [1]
- Φινεύς από τη Φοινίκη, γιος του Αγήνορα, τυφλός βασιλιάς και μάντης [2]
- Πόλτυς, γιος του Ποσειδώνα [3]
- Πυρηνέας απεβίωσε προσπαθώντας να βλάψει τις Μούσες
- Αρπάλυκος, [4] βασιλιάς των Αμυμναίων
- Θόας, ιδρυτής των Τυάνων
- Μόψος, σκότωσε τη Μύρινα, μια βασίλισσα των Αμαζόνων
- Πείροος, Θράκας πολεμιστής [5], που σκοτώθηκε από τον Θόα τον Αιτωλό
- Ρήσος της Θράκης, απεβίωσε στον Τρωικό πόλεμο [6]
- Κισσέας, πατέρας της Θεανώς, συζύγου του Αντήνορα
- Διομήδης ο Θράκης, Γίγαντας που κυβέρνησε τους Βίστωνες
- Λυκούργος, των Ηδωνών
- Οίαγρος, πατέρας του Ορφέα και του Λίνου
- Ορφέας [7] των Κικόνων
- Πολυμήστωρ των Βιστωνίων [8]
- Ζάλμοξις των Γετών
- Κάρναβος των Γετών, ο οποίος ήρθε στην εξουσία, όταν δόθηκε για πρώτη φορά το σιτάρι στους ανθρώπους [9]. Αναφέρεται από τον Σοφοκλή [10]
- Πυραίχμης των Παιόνων
- Αστεροπαίος των Παιονίων
Πέρσες
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]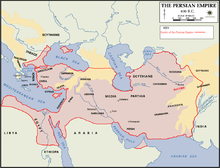
- Δαρείος Α΄, περσική Σατραπεία που ονομάστηκε Σκύδρα το 516 π.Χ. [11]
- Δαρείος Α΄, η Θράκη υποτάσσεται εκ νέου από τον Μαρδόνιο το 492 π.Χ.
- Ξέρξης Α΄ διατηρεί τη Θράκη από το 486 π.Χ. έως το 479 π.Χ.
Βασιλείς φυλών
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]
- Όλορος, 5ος αι. π.Χ. [12]
- Σύρμος, βασιλιάς των Τριβαλλών [13] 4ος αι. π.Χ.
- Βεργαίος, μικρός βασιλιάς του Παγγαίου
- Δρομιχαίτης, των Γετών 300 π.Χ.
- Λάγγαρος, των Αγριανών
- Πλευράτος, Θράκας ή Ιλλυρός βασιλιάς που επιτέθηκε στην Τύλη 213–208 π.Χ.
- Διήγυλις, οπλαρχηγός των Καινών εξαιρετικά αιμοδιψής 145 π.Χ.
- Ζιβέλμιος, γιος του Διηγύλη
- Μόστις, των Καινών, βασιλιάς π. 130–90 π.Χ.
- Αβρούπολις των Σαπαίων, 2ος αι. π.Χ.
- Ραβοκέντης [14] των Bησσών που αναφέρει ο Μ. Τ. Κικέρων
- Κοσίνγας, [15] αρχηγός και ιερέας της Ήρας στις φυλές Κεβρηνών και Συκαιβοών
- Γέτας, βασιλιάς [16] [17] των Ηδονών
Κέλτες και Δάκες
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]
- Κάρναβος, βασιλιάς των Γετών όπως αναφέρει ο Σοφοκλής στο έργο Τριπτόλεμος - 5ος αι. π.Χ.
- Κοθήλας, [18] πατέρας του Μήδας της Οδησσού – 4ος αι. π.Χ.
- Rex Histrianorum, ηγεμόνας στην Ιστρία, που αναφέρεται από τον Τρόγο Πομπήιο και τον Ιουστίνο - 339 π.Χ.
- Διττός – 3ος αι. π.Χ.[ ]
- Mόσκων [19] – 3ος αι. π.Χ.
- Δρομιχαίτης [20] – 3ος αιώνας π.Χ.
- Zαλμοδέγικος [21] – γύρω στο 200 π.Χ. [22]
- Ρέμαξος – γύρω στο 200 π.Χ. [23] [24]
- Ρουβοβόστης [25] – γύρω στο 200 π.Χ.
- Zόλτης - 200 π.Χ. [26]
- Oρόλης [27] – 2ος αι. π.Χ.
- Δικόμης [28] – 1ος αι. π.Χ.
- Ρόλης [29] – 1ος αι. π.Χ.
- Δάπυξ [30] – 1ος αι. π.Χ.
- Ζυράξης [31] – 1ος αι. π.Χ.
- Bουριβίστας [32] – 82–44 π.Χ.
- Δεκηναίος [33] – 44 π.Χ. - γύρω στο 27 π. αρχιερέας
- Θιαμάρκος - 1ος αι. π.Χ. - 1ος αι. μ.Χ., βασιλιάς των Δακών (επιγραφή "Βασιλεύς Θιαμάρκος εποίει") [34]
- Κοτίσος [35] – π. 40 π.Χ. - π. 9 π.Χ.
- Κομοσίκος [36] – 9 π.Χ.–30 μ.Χ.
- Σκορίλος [36] – π.30–70 μ.Χ.
- Κόσων [37]
- Δούρας [37] – π. 69–87.
- Δεκέβαλος [38] – 87–106.
- 106 μ.Χ., η Δακία γίνεται επαρχία της Ρωμαϊκής Αυτοκρατορίας που κατακτήθηκε από τον Τραϊανό.
- Πιέπορος, βασιλιάς των Δακών Κοστοβώκων – 2ος αι. μ.Χ. (αναφέρεται σε επιγραφή) [39] [40]
- Tάρβος – 2ος αι. μ.Χ. Ο Δίων Κάσσιος τον ανέφερε χωρίς να προσδιορίσει την καταγωγή του. Μερικοί συγγραφείς θεωρούν μια πιθανή εθνότητα των Δακών [41] .
Παίωνες
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]
- Βλέπε: Κατάλογος Παιώνων βασιλέων
Κέλτες ηγεμόνες στη Θράκη
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Κερέθριος [42]
- Κριτάσιρος, ένας Κέλτης [43]
- Βαθανάτος [44] [45] των Σκορδίσκων.
Κέλτες ηγεμόνες της Τύλιδος στη Θράκη [46]
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Κομοντόριος Κέλτης στρατιωτικός διοικητής, πρώτος βασιλιάς της Τύλιδος (π. 277 π.Χ.-;)
- Oρσοάλτιος (υποθέτουμε κέλτης με βάση τους τύπους νομισμάτων· η σειρά είναι αβέβαιη)
- Κερσιβάουλος (υποθέτουμε κέλτης με βάση τους τύπους νομισμάτων· η σειρά είναι αβέβαιη)
- Καβάρος, τελευταίος βασιλιάς της Τύλιδος. ανατράπηκε από τους Θράκες (;-212 π.Χ.) [47]
Μακεδόνες
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]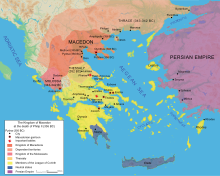
- Φίλιππος Β΄ της Μακεδονίας, προσαρτημένη Θράκη, 341–336 π.Χ
- Μέγας Αλέξανδρος διατηρεί τη Θράκη και καταστέλλει την εξέγερση, 335–323 π.Χ.
- Λυσίμαχος, ένας από τους Διαδόχους, περιλαμβάνει τη Θράκη στο βασίλειό του, 323–281 π.Χ. [48] [49]
- Φίλιππος Ε΄ της Μακεδονίας ελέγχει όλες τις πόλεις της Θράκης μέχρι τον ελλήσποντο, [50] 238–179 π.Χ.
- Περσέας της Μακεδονίας συνεχίζει να ελέγχει το τμήμα της Θράκης που τον άφησε ο πατέρας του, 212–166 π.Χ.
Βασίλειο Οδρυσών
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]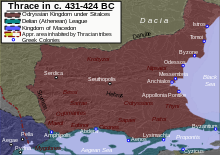

Ο παρακάτω κατάλογος περιλαμβάνει τους γνωστούς Οδρυσίους βασιλείς της Θράκης, αλλά μεγάλο μέρος του είναι από εικασίες, βασισμένος σε ελλιπείς πηγές και στην ποικίλη ερμηνεία των συνεχιζόμενων νομισματικών και αρχαιολογικών ανακαλύψεων. Περιλαμβάνονται και διάφοροι άλλοι Θράκες βασιλείς (μερικοί από αυτούς μη Οδρυσίους). [51] Οι Οδρύσιοι βασιλείς, αν και αποκαλούνταν βασιλείς της Θράκης, δεν άσκησαν ποτέ κυριαρχία σε όλη τη Θράκη. [52] Ο έλεγχος διέφερε ανάλογα με τις φυλετικές σχέσεις. [53] Οδρύσιοι βασιλείς (τα ονόματα παρουσιάζονται με ελληνική μορφή):
- Tήρης Α΄, γιος (;) τού Οδρύση, (480 [54]/450/430 π.Χ. [55])
- Σπαράδοκος, γιος του Τήρη Α΄ (περίπου 465; - έως το 431 π.Χ.)
- Σιτάλκης, γιος του Tήρη Α΄ (από το 431-424 π.Χ.)
- Σεύθης Α΄, γιος του Σπαράδοκου (424-396 π.Χ.)
- Μαισάδης, πατέρας του Σεύθη Β΄, τοπικού άρχοντα στην ανατολική Θράκη
- Tήρης Β΄, τοπικός άρχοντας στην ανατολική Θράκη
- Σαράτοκος (= Σάδοκος, γιος του Σιτάλκη ;), τοπικός άρχοντας στη δυτική Θράκη
- Mήτοκος ( = Aμάδοκος Α΄; ), γιος (;) του Σιτάλκη
- Aμάδοκος Α΄, γιος (;) του Μήτοκου (εκτός αν ταυτίζεται με αυτόν) ή του Σιτάλκη (έως το 405 [56] -μετά το 390 π.Χ.)
- Σεύθης Β΄, γιος του Mαισάδη, απόγονος του Tήρη Α΄, τοπικός άρχοντας στην ανατολική Θράκη (από το 405; - μετά το 387 π.Χ.)
- Ευρύζελμις, γιος ή αδελφός (;) του Σεύθη Α΄ (περίπου 386 π.Χ.)
- Κότυς Α΄ (Οδρυσών), γιος (;) του Σεύθη Α΄ [57] ή Σεύθη Β΄ [58] (από το 384–360 ή το 359 π.Χ.)
- Κερσοβλέπτης, γιος του Κότυ Α΄, βασιλιάς στην ανατολική Θράκη (360 ή 359-341 π.Χ.)
- Βηρισάδης, αντίπαλος του Κερσοβλέπτη, βασιλιάς στη δυτική Θράκη στον Στρίμο (359-352 π.Χ.)
- Αμάδοκος Β΄, γιος του Αμάδοκου Α΄ και αντίπαλος του Κερσοβλέπτη, βασιλιάς στην κεντρική Θράκη στη Χερσόνησο και τη Μαρώνεια (359-351 π.Χ.)
- Κετρίπορις, γιος του Βηρισάδη, βασιλιάς της δυτικής Θράκης στον Στρίμο (358-347 π.Χ.)
- Tήρης Γ΄, γιος (;) του Αμάδοκου Β΄, βασιλιάς στην κεντρική Θράκη στη Χερσόνησο και τη Μαρώνεια (351-342 π.Χ.)
- Οι βασιλείς της Θράκης αναγκάζονται να υποταχθούν στη μακεδονική (επι)κυριαρχία μέχρι το 341 π.Χ.
- Σεύθης Γ΄, γιος (;) του Tήρη Γ΄ [59] ή του Κότυ Α΄, αντιτάχθηκε στη μακεδονική κυριαρχία (από το 324–μετά το 312 π.Χ.)
- Η διαδοχή του Σεύθη Γ΄ είναι ασαφής: η περιοχή μοιράστηκε σε Θράκες δυνάστες και Μακεδόνες βασιλείς, μετά το 277 και από τους Κέλτες της Τύλιδος.
Οδρύσιοι ηγεμόνες στην ανατολική Θράκη (υποθετική διάταξη [60] )
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Κότυς Β΄, γιος του Σεύθη (Γ΄;) (μαρτυρείται το 330 π.Χ., ενώ ήταν ακόμη πρίγκιπας, εάν ήταν γιος του Σεύθη Γ΄;)
- Ραίζδος (Ρόιγος;), γιος (;) του Κότυ Β΄
- Κότυς Γ΄, γιος του Ραίζδου (π. 270 π.Χ.)
- Ρησκούπορις Α΄ (Οδρυσών), γιος του Κότυ Γ΄ (;-από το 212 π.Χ.;) [61]
Οδρύσιοι ηγεμόνες αρχικά στην εσωτερική Θράκη (υποθετική διάταξη [62] )
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Tήρης Δ΄, γιος του Σεύθη (Γ΄;) (π. 295 π.Χ.; )
- Σεύθης Δ΄, γιος του Tήρη (Δ΄;)
- Tήρης Ε΄, γιος (;) του Σεύθη Δ΄ (π. 255 π.Χ.)
- Ρόιγος, γιος του Σεύθη (Δ΄;) (μέσα του 3ου αι., θαμμένος στον Θρακικό τάφο του Kαζανλάκ)
- Σεύθης Ε΄, γιος (;) του Ρόιγου
- Aμάδοκος Γ΄, γιος (;) του Σεύθη Ε΄ (π. 184 π.Χ.)
- Κότυς Δ΄, γιος του Σεύθη Ε΄ (από το 171-μετά το 166)
- Tήρης ΣΤ΄, γιος (;) του Aμάδοκου Γ΄ (π. 148 π.Χ.)
- Bείθυς (Bίθυς), γιος του Κότυ Δ΄ (π. 146 π.Χ.;)
- Η γραμμή μπορεί να συνεχίστηκε ως η δυναστεία των Οδρυσών-Ασταίων, που αναφέρονται παρακάτω.
Διάφοροι Θράκες τοπικοί ηγεμόνες μαρτυρούνται τον 3ο αι. π.Χ. [63]
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Σπάρτοκος, ηγεμόνας της Καβύλης; (π. 295 π.Χ.)
- Σκόστοκος, ηγεμόνας στη νότια Θράκη κοντά στην Αίνο και τη Σηστό (π. 280-μετά το 273 π.Χ.)
- Σαδάλας, ηγεμόνας κοντά στη Μεσημβρία (π. 275 π.Χ.), απόγονος των Κότυ, Mηδίστα, Tαρούντιου και Moπσυέστη (άγνωστη σειρά και σχέσεις)
- Oδορόης (π. 280-273 π.Χ.) (? )
- Αδαίος, Θράκας ή Μακεδόνας ηγεμόνας κοντά στη Κύψελα (π. 260-π. 240 π.Χ.)
Διάφοροι μη Οδρύσιοι ηγεμόνες στη Θράκη [64]
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Αβρούπολις των Σαπαίων πολέμησε με την Μακεδονία των Αντιγονιδών (197-172 π.Χ.)
- Aύτλησβις των ; Καινών, πολέμησε με τον Κότυ Β΄ ως σύμμαχος των Ρωμαίων (π. 168 π.Χ.)
- Διήγυλις των Καινών (από το 150-μετά το 144 π.Χ.)
- Ζιβήλμιος των Καινών, γιος του Διηγυλίδα, δολοφονήθηκε (π. 141 π.Χ.)
- Σόθιμος των ; Μαίδων, σύμμαχος του Μιθραδάτη ΣΤ΄, εισέβαλε στη Ρωμαϊκή Μακεδονία (π. 89 π.Χ.)
Ιλλυριοί ηγεμόνες [65]
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Πλευράτος Α΄ ηγεμόνας κοντά στη Σκόδρα (πριν από το 250 π.Χ.)
- Άγρων, γιος του Πλεύρατου Β' (περ. 250-230 π.Χ.)
- Πίννης, γιος του Άγρωνος (230-212 π.Χ.); επί αντιβασιλείας της θετής μητέρας Τεύτας 230-228 π.Χ. και του θετού πατέρα Δημητρίου εκ Φάρου 228-219 π.Χ.
- Σκερδιλαΐδας, γιος του Πλεύρατου Α΄ (212-206 π.Χ.)
- Πλευράτος Β΄, γιος του Σκερδιλαΐδα (συγγενής 212, 206-180 π.Χ.) [66]
- Γένθιος (Γέντιος), γιος του Πλευράτου Β΄ (180-168 π.Χ.)
- 168 π.Χ. Η Ιλλυρία προσαρτήθηκε από τη Ρωμαϊκή Δημοκρατία
Βασίλειο Οδρυσών-Ασταίων
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]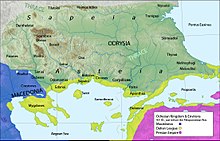
Μία πιθανή συνέχιση της προηγούμενης μοναρχίας των Οδρυσών υπό μια γραμμή βασιλέων, που βασίλευαν από τη Βιζύη (τώρα Βίζε) στην ανατολική Θράκη. [67]
- Κότυς Ε΄, γιος (;) του Bειθύου (;-έως το 87 π.Χ.)
- Σαδάλας Α΄ , γιος του Κότυ Ε΄(από το 87–μετά το 79 π.Χ.)
- Αμάδοκος, βασιλιάς των Οδρυσών, εστάλη προς βοήθεια του Σύλλα στη Χαιρώνεια το 86 π.Χ.
- Κότυς ΣΤ΄, γιος τού Σαδάλα Α΄ (από το 57–48 π.Χ.) [68]
- Σαδάλας Β΄, γιος του Κότυ ΣΤ΄ (48–42 π.Χ.)
- Σαδάλας Γ΄, συγγενής (γιος;) το Σαδάλα Β΄ (42-31 π.Χ.)
- Κότυς Ζ΄, γιος του Σαδάλα Β΄ από την Πολεμοκράτια (31–18 π.Χ.)
- Ρησκούπορις Β΄ (Ασταίων), γιος του Κότυ Ζ΄, που σκοτώθηκε από τους Bησσούς (18–11 π.Χ.)
- 11 π.Χ. Η Ασταία Θράκη παρύαχωρήθηκε στον εκ μητρός θείο τού Ρησκούπορι Β΄, τον Ροιμητάλκη Α΄ βασιλιά των Σαπαίων, από τον Ρωμαίο Αυτοκράτορα Αύγουστο· έτσι ενοποιήθηκε η Θράκη [69].
Βασίλειο των Σαπαίων και ενωμένη Θράκη
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]
Αρχικά μια τοπική δύναμη στην περιοχή της Ροδόπης της νότιας Θράκης, οι Σαπαίοι βασιλείς αυξήθηκαν σε δύναμη και επιρροή και, με τη ρωμαϊκή ευλογία, βρέθηκαν κύριοι ενός ενοποιημένου βασιλείου της Θράκης από το 11 π.Χ. μέχρι τη ρωμαϊκή προσάρτηση το 46 μ.Χ. [70]
- Κότυς Α΄ (Σαπαίων), γιος (;) του Ροιμητάλκη, ;– έως το 48 π.Χ.
- Ρησκούπορις Α΄, γιος του Κότυ Α΄, από το 48 π.Χ.–41 π.Χ.
- Ράσκος, γιος του Κότυ Α΄, συνεργάτης κυβερνήτης; π. 42 π.Χ.
- Κότυς Β΄ (Σαπαίων), γιος του Ρησκούπορι Α΄ (Σαπαίων), 42 π.Χ.–31 π.Χ.
- Η Θράκη γίνεται ενιαίο πελατειακό κράτος της Ρώμης το 11 π.Χ. [71]
- Ροιμητάλκης Α΄, γιος του Κότυ Β΄ (Σαπαίων), 31 π.Χ.–12 μ.Χ. (μονάρχης όλης της Θράκης από το 11 π.Χ.) [72] Νυμφεύτηκε την Πυθοδωρίδα Α΄.
- Ρησκούπορις Β΄ (Σαπαίων), γιος του Κότυ Β΄ (Σαπαίων), στη δυτική Θράκη, καθαιρέθηκε από τον Ρωμαίο Αυτοκράτορα Τιβέριο Α΄, 12–19.
- Κότυς Γ΄ (Σαπαίων), γιος του Ροιμητάλκη Α΄, στην ανατολική Θράκη, σκοτώθηκε από τον θείο του Ρησκούπορι Β΄ (Σαπαίων), 12–19.
- Ροιμητάλκης Β΄, γιος του Κότυ Γ΄, 19-38
- Αντωνία Τρύφαινα - συγκυβέρνησε με τον γιο της Ροιμητάλκη Β΄ [73].
- Οι τελευταίοι πελάτες ηγεμόνες της Θράκης ήταν η βασίλισσα Πυθοδωρίς Β΄ και ο βασιλιάς Ροιμητάλκης Γ΄. [74] Ο Ροιμητάλκης Γ΄, γιος του Κότυ Γ΄ και της Tρύφαινας του Πόντου, 38-46;, νυμφεύτηκε την ανιψιά του Πυθοδωρίδα Β΄ (κόρη του Ροιμητάλκη Β΄ και της Πυθοδωρίδας Α΄). Δολοφονήθηκε από τη σύζυγό του.
- 46 προσάρτηση στη Ρωμαϊκή Αυτοκρατορία, από τον Ρωμαίο Αυτοκράτορα Κλαύδιο Α΄.
Σκύθης
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Σπαργαπείθης, [75] βασιλιάς των Αγαθυρσίων
Δείτε επίσης
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Βασίλειο Οδρυσίων
- Σαπαίοι
- Παιονία
- Κατάλογος των αρχαίων πόλεων της Θράκης
- Κατάλογοςτων αρχαίων φυλών στη Θράκη
- Κατάλογος των ηγεμόνων της Ιλλυρίας
- Κατάλογος των αρχαίων πόλεων στην Ιλλυρία
- Κατάλογος των αρχαίων φυλών στην Ιλλυρία
Σημειώσεις
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- ↑ Tereus, "Tereus 1 is the cruel Thracian king who helped King Pandion 2 of Athens in his war against King Labdacus 1 of Thebes, and having received one of his daughters seduced the other"
- ↑ Phineus, "Phineus is the blind king and seer"
- ↑ Poltys, "Poltys. An Aenian who entertained Heracles when he came to Aenus in Thrace. He was son of Poseidon [Apd.2.5.9]."
- ↑ Harpalyce(Ἁρπαλύκη)., "1. A daughter of Harpalycus, king of the Amymnaeans in Thrace. As she lost her mother in her infancy, she was brought up by her father with the milk of cows and mares, and was trained in all manly exercises. After the death of her father, whom she had once delivered from the hand of the Myrmidons, she spent her time in the forests as a robber, being so swift in running that horses were unable to overtake her. At length, however, she was caught in a snare by shepherds, who killed her. (Serv. ad Virg. Aen. 1.321; Hyg. Fab. 193.)"
- ↑ Peiros, Peiros. Thracian leader, son of Imbrasus and father of Rhigmus. He was killed by Thoas, Leader of the Aetolians (Hom.Il.4.520ff., 20.484ff.).
- ↑ Rhesus Rhesus 2 is chiefly remembered because he came from Thrace to defend Troy with great pomp and circumstance, but died on the night of his arrival, without ever engaging in battle.
- ↑ Carlos Parada, "Orpheus, king of the Ciconians"
- ↑ Polymestor, "Polymestor 1 (Polymnestor). This is the king of the Bistonians in Thrace"
- ↑ Carnabon, "Carnabon. King of the Getae in Thrace who came into power when grain was first given to men [see also Lyncus, and CONSTELLATIONS] [Hyg.Ast.2.14]."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 41: "... Trixae and Sophocles (Triptolem, FR 547) mentions a local king, Charnabon, as a typical anti-hero."
- ↑ The Oxford Classical Dictionary by Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth, (ISBN 0-19-860641-9), page 1515, "The Thracians were subdued by the Persians by 516"
- ↑ The Histories by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, page 373: "... 500 mercenaries, and married Hegesipyle, daughter of the Thracian King Olorus."
- ↑ Plutarch's Lives by Plutarch, 2008, (ISBN 1-4404-1432-7), page 183: "... Danube, and by winning a signal victory over Syrmus, the King of the Triballi. After this, as he heard that the Thebans had revolted, ..."
- ↑ The Oxford Classical Dictionary by Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth, 2003, page 1515: "... *Calpurnius Piso Caesoninus, and *Cicero calls Rabocentus, chief of the Bessi, a faithful ally, although hitherto they had been troublesome ..."
- ↑ Polyaenus: Stratagems - BOOK 7, The generals of the Cebrenii and Sycaeboae, two Thracian tribes, were chosen from among the priests of Hera. Cosingas, according to the tradition of the country, was elected to be their priest and general; but the army took some objection to him, and refused to obey him. To suppress the rebelliousness that had taken hold of the troops, Cosingas built a number of long ladders, and fastened them one to another. He then put out a report, that he had decided to climb up to heaven, in order to inform Hera of the disobedience of the Thracians. The Thracians, who are notoriously stupid and ridiculous, were terrified by the idea of their general's intended journey, and the resulting wrath of heaven. They implored him not to carry out his plan, and they promised with an oath to obey all of his future commands.
- ↑ The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, (ISBN 0-19-815047-4), page 106
- ↑ Ancient Coins of Greek Cities and Kings: From Various Collections Principally in Great Britain by James Millingen, 2004, page 42: "... silver mines so renowned in history. A coin of Geta, king of the Edones, with the legend FETAI HAONEON BAIIAEYI of the same types, ..."
- ↑ Atlas of Classical History by R. Talbert, 1989, page 63, "Getae under Cothelas"
- ↑ https://revistapontica.files.wordpress.com/2012/02/pontica-3-pag-125-129.pdf Radu Ocheșeanu: Monedele basileului Moskon aflate în colecțiile Muzeului de Arheologie Constanța
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, Index Dromichaetes King of the Getians
- ↑ McGing B.C.: The foreign policy of Mithridates VI Eupator, King of Pontus
- ↑ Kurt W. Treptow and Ioan Bolovan in “A history of Romania - East European Monographs”, 1996, (ISBN 9780880333450), page 17 "..Two inscriptions discovered at Histria indicate that Geto-Dacian rulers (Zalmodegikos and later Rhemaxos) continued to exercise control over that city-state around 200 BC ...."
- ↑ The Hellenistic Age from the Battle of Ipsos to the Death of Kleopatra VII by Stanley M. Burstein, 1985, Index Rhemaxos Getic or Scythian ruler
- ↑ Kurt W. Treptow and Ioan Bolovan in “A history of Romania - East European Monographs”, 1996, (ISBN 9780880333450), page 17 "Two inscriptions discovered at Histria indicate that Geto-Dacian rulers (Zalmodegikos and later Rhemaxos) continued to exercise control over that city-state around 200 BC ...."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, Index Rubobostes Dacian King
- ↑ Theodossiev, Nikola (2010). «Thrace». Στο: Gagarin, Michael. The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece and Rome. 1. Oxford University Press. σελ. 55. ISBN 978-0-19-517072-6.
Η παράμετρος |access-date=χρειάζεται|url=(βοήθεια) - ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 53, "Dacian King Oroles"
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 47, "Dicomes of the Getians"
- ↑ The Roman History: The Reign of Augustus by Cassius Dio, Ian Scott-Kilvert, and John Carter, 1987, page 85: "... Then he completed their destruction with the help of Roles, the king of a tribe of the Getae. When Roles visited Octavian, he was treated as a friend ..."
- ↑ Cassius Dio. Roman History, Book LI. "While he was thus engaged, Roles, who had become embroiled with Dapyx, himself also king of a tribe of the Getae, sent for him. Crassus went to his aid, and by hurling the horse of his opponents back upon their infantry he so thoroughly terrified the latter also that what followed was no longer a battle but a great slaughter of fleeing men of both arms. Next he cut off Dapyx, who had taken refuge in a fort, and besieged him. In the course of the siege someone hailed him from the walls in Greek, obtained a conference with him, and arranged to betray the place. The barbarians, thus captured, turned upon one another, and Dapyx was killed along with many others. His brother, however, Crassus took alive, and not only did him no harm but actually released him."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 146, "Zyraxes who ruled in Dobruja"
- ↑ Studies in Ancient Greek and Roman Society by Robin Osborne, 2004, page 128: "... of its citizens, named Akornion, went on an embassy to Burebista, the first and greatest of the kings in Thrace..."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, Index (Decaeneus/Dekaineus/Dicineus) Dacian High priest"
- ↑ Berciu 1981, σελ. 139-140.
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 48, "The Dacian king Cotiso"
- ↑ 36,0 36,1 Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 72, "At least two of his successors Comosicus and Scorillo/Corilus/Scoriscus became high priests and eventually Dacian kings"
- ↑ 37,0 37,1 Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 47, "Kings Coson (who minted his own coins) and Duras"
- ↑ De Imperatoribus Romanis . Retrieved 2007-11-08. "In the year 88, the Romans resumed the offensive. The Roman troops were now led by the general Tettius Iulianus. The battle took place again at Tapae but this time the Romans defeated the Dacians. For fear of falling into a trap, Iulianus abandoned his plans of conquering Sarmizegetuza and, at the same time, Decebalus asked for peace. At first, Domitian refused this request, but after he was defeated in a war in Pannonia against the Marcomanni (a Germanic tribe), the emperor was obliged to accept the peace."
- ↑ Wilhelm Tomachek in “Les restes de la langue dace” published in “Le Muséon By Société des lettres et des sciences, Louvain, Belgium, page 407 "Pieporus, prince des daces Costoboces..."
- ↑ Gudmund Schütte in Ptolemy's maps of northern Europe, H. Hagerup, 1917 page 82 "historical king Pieporus. The same author Schütte in “Our forefathers” published by University Press, 1929 page 74 "The North Dacian tribes of the Koistobokoi and Karpoi unlike the rest of Dacia escaped the Roman conquest of AD 105..."
- ↑ Wilhelm Tomachek (1883): “Les restes de la langue dace” published in “Le Muséon By Société des lettres et des sciences, Louvain, Belgium, page 409
- ↑ The Oxford Illustrated History of Prehistoric Europe (Oxford Illustrated Histories) by Barry Cunliffe, 2001, page 380
- ↑ Strabo, Geography(7.5.2), "A part of this country was laid waste by the Dacians when they subdued the Boii and Taurisci, Celtic tribes under the rule of Critasirus"
- ↑ The Ancient Celts by Barry Cunliffe, (ISBN 0-14-025422-6), 2000, page 86: "... distinguished suggests that one of the returning groups, led by Bathanatos, finally settled in the Middle Danube region at the confluence ..."
- ↑ Celts - a History, The by Daithi O HOgain, (ISBN 1-905172-20-6), 2006, page 60, "... those who, on their return from Greece under their leader Bathanatos, had settled at the confluence of the Danube and the ..."
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan. Compare Werner 1961: 115, 239
- ↑ Celts and the Classical World by David Rankin, (ISBN 0-415-15090-6), 1996, page 189: "According to Polybius, the last of the kings of Tylis, Cavarus, was a man of magnanimity and regal character" (8.24).
- ↑ Heckel, Waldemar. Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great: Prosopography of Alexander's Empire. Blackwell Publishing, 2006, (ISBN 1-4051-1210-7), p. 155. "In 306 or 305, he assumed the title of "King", which he held until his death at Corupedium in 282/1."
- ↑ Heckel, Waldemar. Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great: Prosopography of Alexander's Empire. Blackwell Publishing, 2006, (ISBN 1-4051-1210-7), p. 155. "In 323 Lysimachus was assigned control of Thrace, and was probably strategos rather than satrap. The subordinate position of strategos may account for the failure of the sources to mention Lysimachus in the settlement of Triparadeisus; his brother Autodicus was, however, named as a Somatophylax of Philip III at that time
- ↑ The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 by Christopher Webber, (ISBN 1-84176-329-2), 2001, page 11, "Philip V of Macedon occupied all the cities in Thrace up to the Hellespont, "
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan. Compare Werner 1961: 111-114, 239-240; Topalov 1994.
- ↑ The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald,1998, (ISBN 0-19-815047-4), page 105
- ↑ The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald,1998, (ISBN 0-19-815047-4), page 107
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan.
- ↑ Thrace. The History Files.
- ↑ Smith, William (1867). "Amadocus (I)". In William Smith. Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology 1
- ↑ Topalov 1994
- ↑ Archibald 1998
- ↑ Topalov 2001: 272-278
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan. Compare Werner 1961: 114-115, 239
- ↑ Manov 2015 dates the coins and inscription naming "Rhescuporis son of Cotys" to the beginning of the First Century AD and argues that they are the Sapaean Cotys III and his uncle Rhescuporis II/III. While a later date for this Rhescuporis and his father Cotys may be advisable (and therefore this Cotys would be distinct from Cotys son of Rhaezdus), Manov's hypothesis contradicts the father-son relationship between Cotys and Rhescuporis in the sources.
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan, who also gives an alternative sequence should Rhoegus be placed in the early Third Century BC: "But if Roigos is dated to the early 3rd century and was a son of Seuthēs III (e.g., Kojčev 2008), the pedigree and succession could be restored as follows: Seuthēs III–Roigos–Seuthēs IV–Tērēs IV–Seuthēs V; our Tērēs VI would become Tērēs V." Compare Werner 1961: 114-117, 239.
- ↑ Jurukova 1992: 105-152.
- ↑ Werner 1961: 115-119, 239.
- ↑ Werner 1961: 90-93, 241.
- ↑ The History Of Rome by Livy, 2004, (ISBN 1-4191-6629-8), page 27: "Pleuratus and Scerdilaedus might be included in the treaty. Attalus was king of Pergamum in Asia Minor; Pleuratus, king of the Thracians;
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan; Werner 1961: 117-119, 239, 242; Sullivan 1990: 25-30, 145-151, stemma 1.
- ↑ Kessler, P L. «Kingdoms of Greece - Sapes (Thrace)». www.historyfiles.co.uk.
- ↑ Tačeva 1997: 83-95, 246-247, develops an alternative to the long-dominant reconstruction of the political, chronological, and genealogical relationships reflected in this list (established by Dessau in 1913 and widely accepted, e.g., Sullivan 1990), having the Odrysian-Astaean line end with Sadalas II in 42 BC, making Cotys VII the brother (not brother-in-law) of the Sapaean Rhoemetalces I, and identifying Cotys VII's son Rhescuporis II (not Rhoemetalces I's brother, the Sapaean Rhescuporis II) as the father of Rhoemetalces II. Despite some improbabilities, this reconstruction has gained some acceptance at least as a viable alternative. A variation on this reconstruction by Delev 2016b accepts ending the Odrysian-Astaean line with Sadalas II (whom he combines with Sadalas III to end c. 31 BC), followed by Cotys VII, older brother (not brother-in-law) of the Sapaean Rhoemetalces I, and father of Rhescuporis II, but not grandfather of Rhoemetalces II (who would remain son of the Sapaean Rhescuporis II/III, the younger brother of Rhoemetalces I). In Delev 2016a, the same author posits that Cotys VII need not have reigned.
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan; Werner 1961: 118-120, 239, 242; Sullivan 1990: 25-30, 145-151, stemma 1.
- ↑ Mladjov, Thracian Kings, University of Michigan, "On the death of the last Astaean king in 11 BC, the Roman emperor Augustus conferred all of Thrace on the dead king’s Sapaean uncle Roimētalkēs I. In AD 46, on the murder of Roimētalkēs III by his wife, the kingdom of Thrace was annexed as a province by the Roman emperor Claudius I."
- ↑ Tačeva 1997: 83-95, 246-247, develops an alternative to the long-dominant reconstruction of the political, chronological, and genealogical relationships reflected in this list (established by Dessau in 1913 and widely accepted, e.g., Sullivan 1990), having the Odrysian-Astaean line end with Sadalas II in 42 BC, making Cotys VII the brother (not brother-in-law) of the Sapaean Rhoemetalces I, and identifying Cotys VII's son Rhescuporis II (not Rhoemetalces I's brother, the Sapaean Rhescuporis II) as the father of Rhoemetalces II. Despite some improbabilities, this reconstruction has gained some acceptance at least as a viable alternative. A variation on this reconstruction by Delev 2016b accepts ending the Odrysian-Astaean line with Sadalas II (whom he combines with Sadalas III to end c. 31 BC), followed by Cotys VII, older brother (not brother-in-law) of the Sapaean Rhoemetalces I, and father of Rhescuporis II, but not grandfather of Rhoemetalces II (who would remain son of the Sapaean Rhescuporis II/III, the younger brother of Rhoemetalces I). In Delev 2016a, the same author posits that Cotys VII need not have reigned. If Delev's reconstruction is correct, the Sapaean unification of Thrace would be under Cotys II in 31 BC, and he would be followed by his grandson Rhescuporis II, then the latter's uncle and guardian (Cotys II's son) Rhoemetalces I, the remaining relationships remaining unchanged from the ones indicated in this list, except perhaps for the numeration of rulers named Cotys and Rhescuporis.
- ↑ «Antonia Tryphaena». British Museum. Ανακτήθηκε στις 1 Σεπτεμβρίου 2022.
- ↑ Miszczak, Izabela (10 Μαρτίου 2021). Edirne: Gateway to the Balkans (στα Αγγλικά). ASLAN Izabela Sobota-Miszczak. ISBN 978-83-956540-6-0.
- ↑ Readings in Greek History: Sources and Interpretations by D. Brendan Nagle and Stanley M. Burstein, (ISBN 0-19-517825-4), 2006, page 26: "... Ariapeithes, the Scythian king, had several sons, among them, ... by Spargapeithes, king of the Agathyrsi; whereupon Scylas succeeded to the throne, and married one of ..."
Bιβλιογραφικές αναφορές
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- The Histories, μετάφραση GC Macaulay, Barnes & Noble, Inc., 2004.
- Z. Archibald, The Odrysian kingdom of Thrace, Οξφόρδη, 1998.
- P. Delev, «Cotys son of Rhascuporis», στο: M. Slavova, N. Šarankov (επιμ. ), Studia Classica Serdicensia V. Μνημεία και Κείμενα στην Αρχαιότητα και όχι μόνο. Δοκίμια για την εκατονταετηρίδα του Georgi Mihailov (1915-1991), Σόφια, 2016a: 119-129.
- P. Delev, "Za genealogijata na Sapejskata dinastija" στο: P. Delev (επιμ. ), Συμπόσιο. Μελέτες στη μνήμη του καθ. Ντιμίταρ Ποπόφ , Σόφια, 2016β: 148-173.
- H. Dessau, «Reges Thraciae qui fuerint imperante Augusto», Ephemeris Epigraphica 9 (1913) 696-706.
- J. Jurukova, Monetite na trakijskite plemena i vladeteli, τόμ. 1., Σόφια, 1992.
- M. Manov, «Dekret na Apolonija s novo datirane» , Numizmatika, Sfragistika i Epigrafika 11 (2015) 167-173.
- RD Sullivan, Near Eastern Royalty and Rome, 100-30 π.Χ., Τορόντο, 1990.
- M. Tačeva, Istorija na bălgarskite zemi v drevnostta prez elinističeskata i rimskata epoha, Σόφια, 1997.
- S. Topalov, The Odrysian Kingdom from the Late 5th to the Mid-4th CBC, Σόφια, 1994.
- S. Topalov, Συνεισφορές στη μελέτη της νομισματοκοπίας και της ιστορίας στα εδάφη της Ανατολικής Θράκης από το τέλος του 4ου CBC έως το τέλος του 3ου CBC, Σόφια, 2001.
- R. Werner, στο: W.-D. von Barloewen (επιμ. ), Abriss der Geschichte antiker Randkulturen, Μόναχο, 1961: 83-150, 239-242.
